
- Using ssh on mac how to#
- Using ssh on mac software#
- Using ssh on mac password#
- Using ssh on mac windows#
Using ssh on mac password#
Lastly, enter the password to unlock the key: The command brings up a prompt for entering the private key password: In Linux, use this command to copy the key automatically: ssh-copy-id output shows the number of keys automatically copied to the server along with further instructions.įor transferring files via SSH, multiple solutions exist:Īfter generating and copying the keys, log into your server from the local machine using the following command: ssh If you do not specify a username, SSH uses the currently logged in user. For multiple users and keys, copy each new key onto a new line. Copy the public key contents into the authorized_keys file. Next, open the authorized_keys file using a text editor. Create a file called authorized_keys in the ~/.ssh directory: touch authorized_keysĬhange the permissions: chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keysģ. Next, change the permissions with: chmod 700 ~/.sshĢ. If the directory is non-existent, create the folder: mkdir ~/.ssh On the server machine, check if the ~/.ssh folder exists: ls -l ~/.ssh/ Configuring one or multiple SSH/SFTP Users for Your KeyĪfter generating a key pair, the next step is to configure the server machine for SSH and SFTP users for the key.ġ. Re-enter the same passphrase and press Enter to finish generating the key pair. Enter the passphrase to encrypt the private key.
Type Y to confirm and press Enter to continue the setup.Ĥ. If keys exist in this location, the output asks to confirm the overwrite. Otherwise, press Enter to save the keys in the default path. If you set up a specific location for the keys, type in the path now.
Using ssh on mac windows#
Try following our detailed tutorial for generating an SSH key pair on Windows 10.ģ. There are other ways to generate the keys. The command starts the program for generating the key pair. Use the Windows search box to find cmd and open the Command Prompt window. Confirm the keys are in the directory by checking the contents: ls -l ~/.ssh/ġ. Additionally, a digital and a graphic representation print to the console too.Ĩ. Lastly, the program prints out information about where the keys are stored. The password is required any time you use the key for authentication.ħ. Press Enter and confirm the passphrase once more when requested. Finally, enter a passphrase to secure the key. If any keys already exist in this location, the program overwrites the data.Ħ. Otherwise, press Enter to save in the default location. If you have existing keys you want to keep, enter a new file name. The default directory and file for key storage is /home//.ssh/id_rsa. Next, the program asks where to save the file: The output prints out a message, indicating the command ran successfully. The following command starts the key generator: ssh-keygen Change the permissions to 700: chmod 700 ~/.sshĥ. Create the directory using the mkdir command for storing the new key pair: mkdir ~/.sshĤ. If there are no existing keys, the output indicates the folder does not exist:ģ. However, stating a new name for the keys saves them to different files. Generating new keys overwrites the current ones by default.

If there are keys already, the output shows the directory contents: Check for existing keys with: ls -l ~/.ssh/id*
Using ssh on mac how to#
How to Generate & Set Up SSH Keys on CentOS 7.Ģ.How to Generate & Set Up SSH Keys on Debian 10.How to Generate SSH Keys on Ubuntu 18.04.Note: For a more detailed OS-specific tutorials, check out our in-depth guides: The basic instructions for Linux, macOS, and Windows are outlined below. Generate the SSH key pair on the local server using OpenSSH.
Using ssh on mac software#
For automation purposes, key management software and practices apply since the private key stays unprotected otherwise.

Adding a passphrase to encrypt the private key adds a layer of security good enough for most user-based cases. The model assumes the private key is secured. The server allows access to anyone who proves the ownership of the corresponding private key.
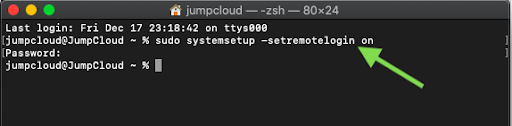
The server stores and marks the public key as approved.Ĥ. Add the corresponding public key to the server.ģ. The private key stays on the local machine.Ģ. Generate a private and public key, known as the key pair. The SSH public key authentication has four steps:ġ. Follow our guides to turn on SSH on Linux: Ubuntu 18.04, Debian 9 or 10. Command line/terminal access with administrator privileges.This guide gives step-by-step instructions on how to implement public key authentication from scratch. Although using a strong password helps prevent brute force attacks, public key authentication provides cryptographic strength and automated passwordless logins. Instead of a password, the procedure uses a cryptographic key pair for validation. Public Key Authentication is a secure logging method using SSH.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
